Table Of Content
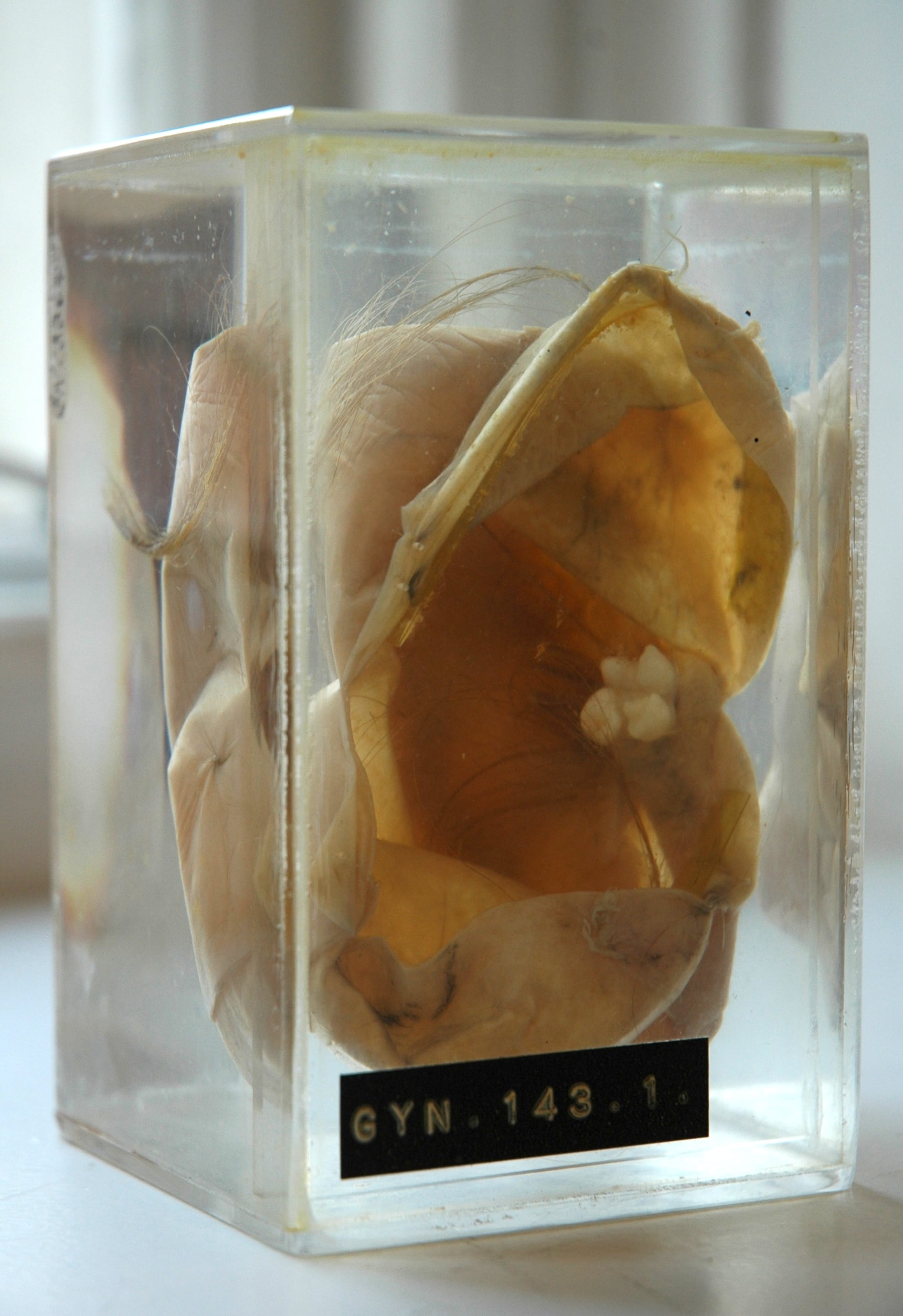
A 38-year-old woman presented with long-lasting dull pain that she localised in her left hip. In the presented MRI (figure 2) the caudal tooth is outlined and an arrow indicates its central pulp. Both teeth belong to a well-demarcated round tumour of 4.5 cm diameter that contains much fat. This fat appears dark due to the fat-suppression of the applied proton density-weighted turbo spin-echo sequence.
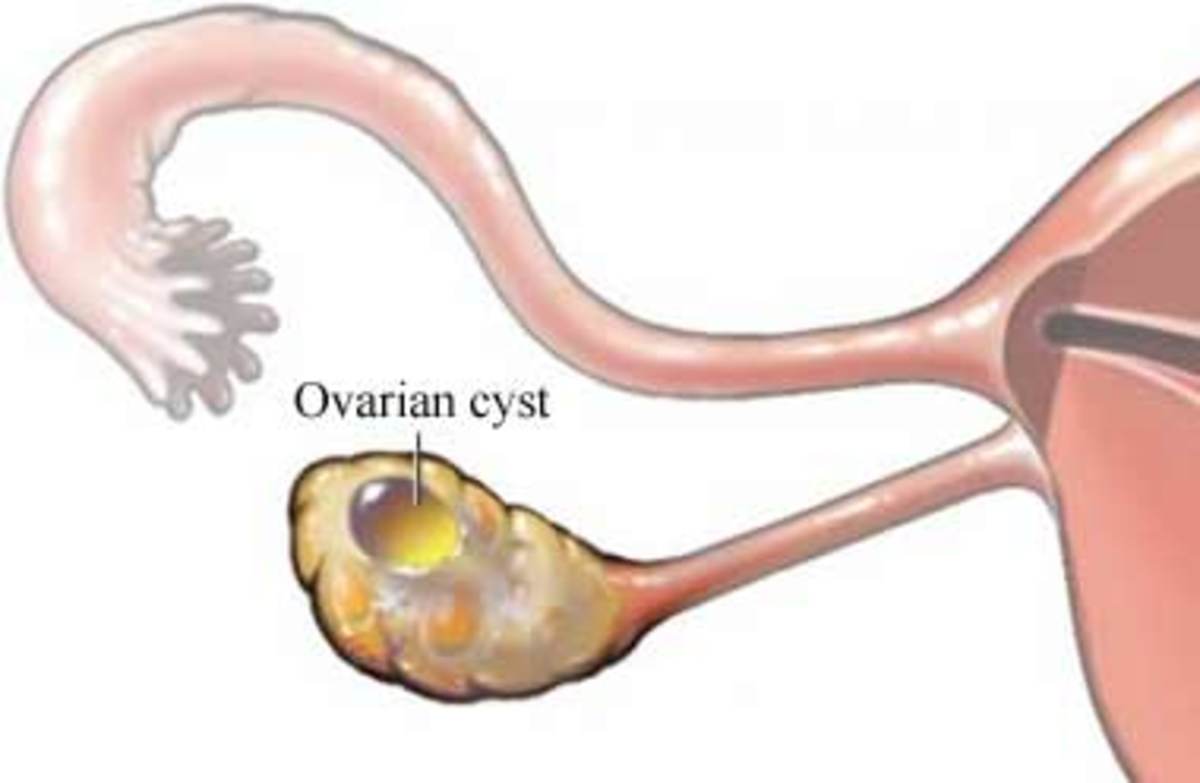
What Is a Dermoid Cyst in the Ovary?
The main symptom can be a dull ache or discomfort related to feeling bloated. Ovarian cysts usually don’t have symptoms, are very small, and go away on their own. But if they get large enough or are in a certain spot, they can cause symptoms. The manner of presentation depends on where exactly the dermoid cyst is. The most likely cause of your cyst depends on several things, including whether you still have a regular menstrual cycle.
Cysts caused by other medical conditions
The most common type of ovarian cyst grows when you ovulate. It happens if the follicle from your ovary either doesn’t release an egg or doesn’t shrink down after releasing an egg, then builds up into a cyst. However, this depends on factors like the size of the cyst and where it is, and about weighing the costs and benefits of removing the cyst, Dr. Khalil explains. So, if you have a dermoid cyst (or any cyst at all, really), a thorough discussion with your doctor can help you decide what to do.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
If they become infected, the infection must be treated and the cyst should be removed. It is easier to remove cysts and prevent scars if the cyst is removed before it gets infected. If dermoid cysts appear on the medial aspect, the possibility of an encephalocele becomes greater and should be considered among the differential diagnoses. SELF does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
The corpus luteum produces estrogen and progesterone and then dissolves if pregnancy does not occur. A corpus luteal cyst happens when excess fluid builds up in the corpus luteum. An ovarian cyst can vary in size from half an inch to 4 inches, and sometimes even much larger. Small cysts less than 5 centimeters across are considered to be benign (non-cancerous).
Your provider may recommend a different surgery called laparotomy if your cyst is especially large, if you have cysts on both ovaries or if the cyst may be malignant. A laparotomy involves a more significant cut into your abdomen. As ovarian dermoid cysts don’t often cause symptoms, you’ll likely learn that you have one during a routine imaging procedure. Your provider may find one during an abdominal or transvaginal ultrasound. Dermoid cysts have a distinctive appearance that makes them easy to identify with imaging. Experienced sonographers (specialists who interpret ultrasound images) can identify dermoid cysts nearly 100% of the time.
Doctors remove huge hairball growing inside 30-year-old woman's ovaries since birth - The Mirror
Doctors remove huge hairball growing inside 30-year-old woman's ovaries since birth.
Posted: Fri, 31 Jan 2020 08:00:00 GMT [source]
However, having polycystic ovaries without PCOS doesn't seem to be linked with fertility problems. Work with your healthcare provider to find a treatment plan that makes sense for you. In some cases, you may need to have follow-up ultrasound tests to determine if your cyst has gone away or is not growing. If you are experiencing severe abdominal or pelvic pain, or pain with fever or vomiting, it is imperative to seek immediate medical attention. A cystadenoma happens when a cyst grows on the surface of the ovary and is filled with a watery or mucous-like material.
Surgery to remove these cysts may also need to remove some or all of the ovary (particularly if they've become large), which can affect fertility. If an ovarian cyst bursts or gets twisted, it can cause sudden, very severe pain. Usually, ovarian cysts are harmless enough that prevention shouldn’t be a concern. Instead, take note of any symptoms that may indicate a cyst and tell your provider about them. Schedule regular pelvic exams so that your provider can find any cysts that require treatment.
Exams and Tests
An ovarian cyst that bursts may cause sudden, serious, one-sided belly or back pain. You may feel lightheaded or weak if a ruptured ovarian cyst causes internal bleeding. Sometimes, they can grow large and cause pain or burst open. And some ovarian cysts make it harder to get pregnant. Functional cysts are the most common type of ovarian cyst and aren’t disease-related. They occur as a result of ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary).
As a result, most teratomas — even cancerous ones — have excellent survival rates with early diagnosis and treatment. A healthcare provider will do a physical examination and ask about your symptoms and medical history. They may also recommend tests to confirm a diagnosis.
These cysts can be a sign that your ovaries are functioning as they should. Functional cysts generally shrink over time, usually within 60 days, without specific treatment. Scheduling regular pelvic exams and speaking with your provider about any symptoms you may be experiencing can help prevent any problems with a cyst.